Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid)
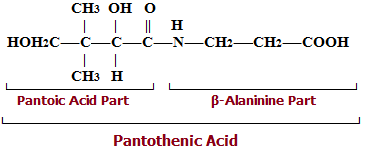
It is viscous yellow oil. It is stable to moist heat but is destroyed by dry heat. It is available commercially as sodium and calcium salts. Its chemical formula is given bellow:
 Occurrence of Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid)
Occurrence of Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid)
It is very widespread and occurs specially in liver kidney, eggs, milk, peas, cauliflower, cabbage, potatoes and tomatoes. The intestinal E –coli also synthesize it and some may be absorbed. It is due to its widespread occurrence that it was named Pantothenic acid (pantos=every where). However, this vitamin is quite unstable.
 Biochemical Role of Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid)
Biochemical Role of Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid)
Pantothenic acid forms a part of the molecule of coenzyme A (CoA-SH) which is concerned with the metabolism of proteins, fats and carbohydrates. Coenzyme A takes part in many physiological reactions, e.g. formation of acetyle-S-CoA and succinyl-S-CoA, in the oxidation of fatty acids and in the utilization of acetoacetic acid, synthesis of cholesterol and in many other biochemical reactions. Coenzyme A can be represented as given below.
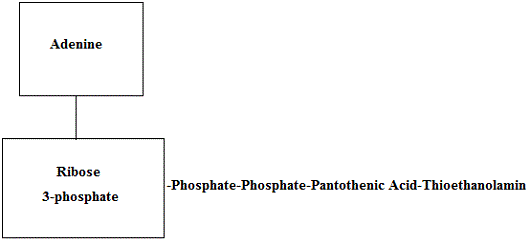
In addition to forming a part of the molecule of Coenzyme A Pantothenic acid also occurs in the molecule of Acyl carrier protein (ACP) which takes part in the biosynthesis of fatty acids.
Folic acid and biotin seem to be needed for the utilization of the vitamin.
 Symptoms of Deficiency of Pantothenic Acid
Symptoms of Deficiency of Pantothenic Acid
The following deficiency symptoms are observed in the experimental deficiency in the rat:
- Reproductive function are seriously affected both in male and female rat.
- Graying of hair (achromotruchia) occurs in black rats; this however, is not specific for the deficiency of this vitamin and also occurs in the deficiency of other factors e.g. inositol. Graying of hair is prevented by adrenalectomy in rats deficiency in this vitamin.
- The cholesterol content of the adrenal cortex is decreased because coenzyme A which take part in cholesterol synthesis is not available in required amounts. The adrenal cortex shows atrophy.
- Porphyrin-caked or bloody whiskers and circumocular loss of hair (spectacle eyes).
- Reduced ability to develop conditioned reflexes.
- Gastrointestinal disturbances including duodenal ulcers.
 Effects of Deficiency of Vitamin B5 in Human Beings
Effects of Deficiency of Vitamin B5 in Human Beings
- Irritability, restlessness, disturbed sleep rhythem and excessive fatigue on mild exercise.
- Gastrointestinal disturbances.
- The response of the adrenal cortex to ACTH is diminished. For example, the eosinopenia seen in normal person after ACTH administration does not take place.
- Burning feet syndrome.
- Greater incidence of respiratory infection and upper abdominal pain.
Daily requirement of Pantothenic acid have not been established though 10 to 15 mg/day is considered sufficient for adults.




