STUDY
AND
EXAM
.COM
Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin)
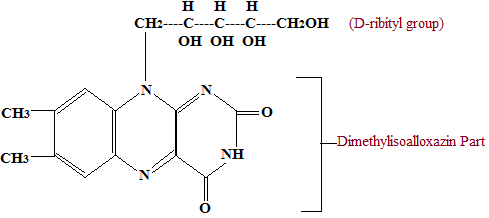
 Occurrence of Vitamin B2
Occurrence of Vitamin B2
This vitamin occurs as free riboflavin or as a constituent of flavoproteins which act as enzymes. It is widely distributed in nature being present in all cells of Plants and animals. Liver, wheat, germs, yeast, milk, meats, fish and eggs are rich sources. Leafy vegetables, fruits and most root vegetables are also good sources while grains and cereals have little of it but they come to have more of it during germination. Vitamin B2 deficiency is usually associated with a low intake of milk and animal proteins. Pasteurization of mil results in an appreciable loss of this vitamin.
 Biochemical Role of Vitamin B2
Biochemical Role of Vitamin B2
Riboflavin forms two coenzymes, FMN and FAD as given below: 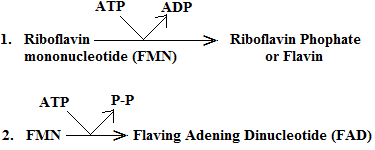
FMN is the coenzyme of cytochrome c reductase, L-amino acid dehydrogenase and Warburg’s Yellow Enzyme. FAD is the coenzyme for xanthine oxidase, liver aldehyde oxidase and acyl-S-CoA dehydrogenase. The enzymes containing riboflavin are called flavoproteins. These enzymes catalyze oxidation-reduction reaction.
 Deficiency Symptoms of Vitamin B2
Deficiency Symptoms of Vitamin B2
No specific deficiency disease is caused by riboflavin deficiency. Ectodermal tissues, i.e. skin, eye, and nervous system are the most vulnerable to its lack. Expermental deficiency in rats has been produced and results in a stoppage of growth, degeneration of nerves and eye disturbances like corneal vascularization and cataracts. There is scaliness of skin and loss of hair. Riboflavin deficiency during pregnancy may produce congenital anomalies in the embryo. In human the following Symptoms are found:
- Inflammation of lips, fissures at the angles of the mouth (cheilosis), scaliness, greasiness and fissures in the folds of ears and nose. The tongue shows inflammation (magneta glossitis) with flattening of papillae.
- Eye disturbances like inflammation and vascularization of cornea, redness of eyes, photophobia, itching, burning and drying of eyes. There is decrease in visual acuity.
BIOCHEMISTRY POSTS




